Best Omega-3 Sources for Dairy-Free Diets
Plant-based omega-3 options for dairy-free diets — flax, chia, hemp, walnuts, soy and algae supplements to supply ALA, EPA and DHA for heart and brain health.

Looking to meet your omega-3 needs without dairy or fish? There are plenty of plant-based options that pack a punch. From flaxseeds to algae-based supplements, these foods can help support heart, brain, and overall health. Here's a quick rundown of the top sources:
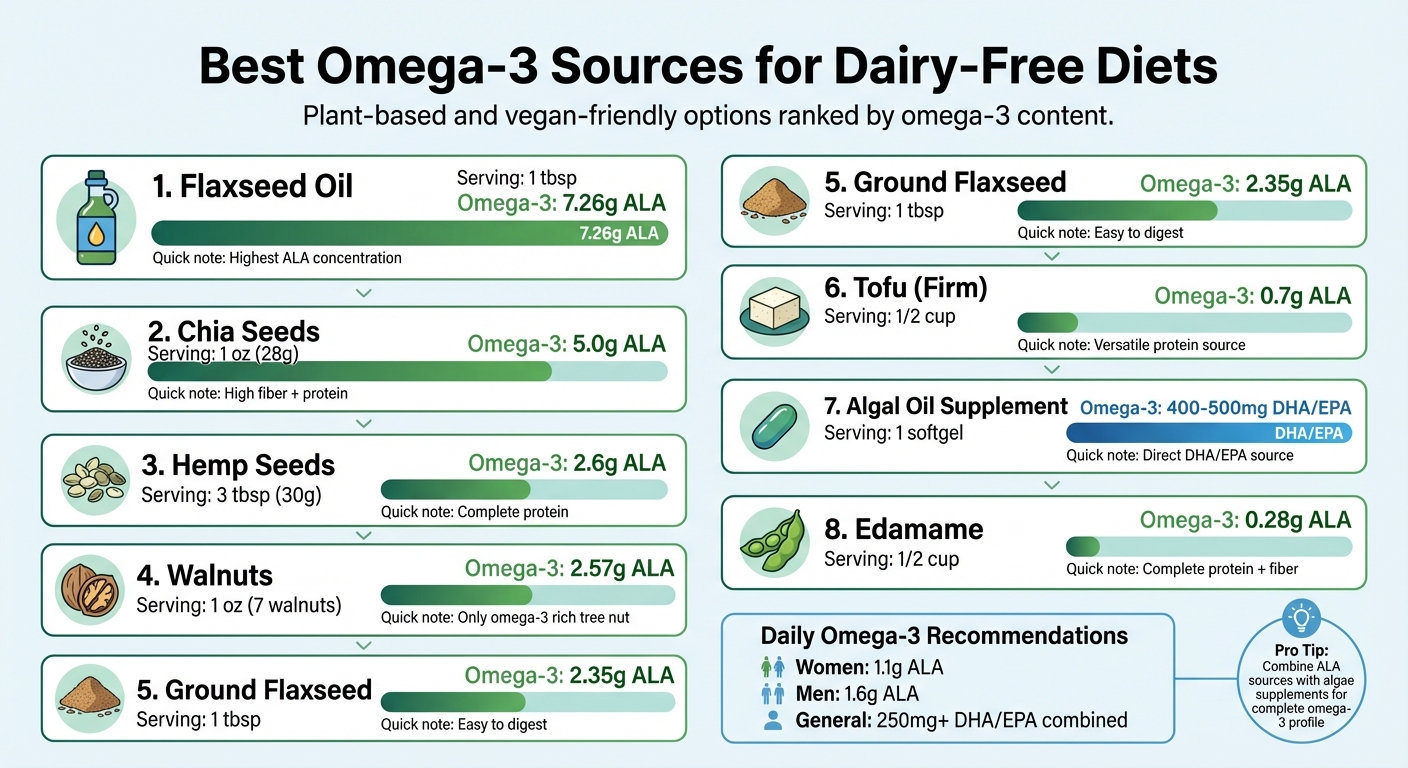
- Flaxseed & Flaxseed Oil: 1 tbsp offers 2.35g–7.26g of ALA. Perfect for smoothies, oatmeal, or salad dressings.
- Chia Seeds: 1 oz delivers 5g of ALA. Use in puddings, salads, or baked goods.
- Hemp Seeds: 3 tbsp provide 2.6g of ALA. Great for smoothies, salads, or as a topping.
- Walnuts: 1 oz contains 2.57g of ALA. Snack on them or add to meals.
- Algae-Based Supplements: Direct source of EPA and DHA, offering 400–1,200 mg per serving.
- Soy Products (Edamame, Tofu): Smaller amounts of ALA but versatile and protein-rich.
Pro Tip: Combine ALA-rich foods with algae-based supplements for a more complete omega-3 profile. Keep reading for easy meal ideas, nutritional benefits, and cost-effective options.
Omega-3 Content Comparison: Top Dairy-Free Sources
1. Flaxseed and Flaxseed Oil
Omega-3 Content per Serving
Flaxseed stands out as the top plant-based source of ALA (alpha-linolenic acid). Here’s how it measures up: one tablespoon of whole flaxseed provides 2.35 grams of ALA, two tablespoons of ground flaxseed offer 3.2 grams, and a single tablespoon of flaxseed oil delivers a whopping 7.26 grams - over four times the recommended daily intake. With such an impressive omega-3 profile, flaxseed is a smart and simple addition to any dairy-free diet.
"Flax delivers more ALA omega-3 fatty acids than any other known food on the planet." – Lauren Wicks, Writer and Editor, EatingWell
Easy Ways to Add Flaxseed to Your Diet
Ground flaxseed is easier to digest than whole seeds, which often pass through the digestive system without being broken down. You can sprinkle ground flaxseed over oatmeal, blend it into smoothies, or mix it into plant-based yogurt. It’s also a fantastic ingredient for dairy-free baking - combine 1 tablespoon of ground flaxseed with 2.5 tablespoons of water to make a flax egg.
Flaxseed oil, on the other hand, works best as a finishing touch. Drizzle it over salads or whisk it into dressings, but avoid cooking with it since it has a low smoke point. Beyond its versatility, flaxseed is both affordable and easy to find, making it an accessible choice for most households.
Availability and Cost
Flaxseed products are widely available, whether you shop online through platforms like Amazon or at your local grocery store. Organic ground flaxseed typically costs around $0.24–$0.26 per ounce.
More Than Just Omega-3s
Flaxseeds don’t stop at omega-3s - they’re packed with fiber (2 grams per tablespoon), protein (2.5 grams per 2-tablespoon serving), and essential minerals like magnesium and manganese. They’re also rich in lignans, which have antioxidant properties. One clinical trial even found that consuming 30 grams of flaxseed daily reduced systolic blood pressure by 13.36 units.
To keep your flaxseed fresh and prevent the oils from going rancid, store ground flaxseed in the refrigerator or freezer. With all these benefits, flaxseed is a powerhouse ingredient that supports omega-3 needs while fitting seamlessly into a dairy-free lifestyle.
2. Chia Seeds
Omega-3 Content per Serving
In just a 1-ounce (28g) serving, chia seeds provide a generous 5,000 mg of ALA - more than enough to meet daily recommendations for both men and women. Prefer measuring by the tablespoon? Each one delivers about 2.53 grams of ALA. While chia seeds are an excellent source of ALA, it’s good to know that only a small percentage of ALA (5–10%) gets converted to EPA, and even less (2–5%) to DHA, the more active omega-3 forms.
Ease of Incorporation into Meals
One of the best things about chia seeds is how easy they are to use. Unlike some seeds, they don’t need to be ground, and their mild, neutral flavor means they can blend seamlessly into almost any dish. For instance, they work as an egg substitute in dairy-free baking. Want a simple breakfast idea? Mix 2 tablespoons of chia seeds with 1/2 cup of plant-based milk and let it sit overnight for a creamy pudding. You can also sprinkle them on oatmeal, blend them into smoothies, or toss them on top of salads and roasted vegetables for added texture and nutrition.
Availability and Affordability
You won’t have to search far to find chia seeds - they’re stocked in most grocery stores, health food stores, and online retailers like Amazon. Prices vary depending on the brand and whether you opt for organic, but they’re generally a budget-friendly way to boost your nutrition.
Additional Nutritional Benefits
Chia seeds pack a punch beyond omega-3s. A single 1-ounce serving offers 9.8 grams of dietary fiber, covering more than one-third of your daily needs, along with 4–5 grams of complete protein that includes all nine essential amino acids. They’re also a good source of calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus, making them a great choice for anyone managing lactose intolerance and looking to support bone health without dairy. On top of that, chia seeds are rich in antioxidants like quercetin and chlorogenic acid, which help protect your cells from oxidative stress. Plus, when combined with liquid, they form a gel-like consistency that can help you feel fuller longer - potentially aiding in weight management. Just be sure to drink plenty of water to avoid any digestive discomfort due to their high fiber content.
3. Hemp Seeds and Hemp Seed Oil
Omega-3 Content per Serving
Hemp seeds are another excellent plant-based source of omega-3s, following flaxseed and chia seeds. A 3-tablespoon (30g) serving of hemp seeds provides 2.6–2.79 grams of ALA (alpha-linolenic acid). If you prefer a smaller portion, 2 tablespoons (20g) still deliver about 1.7 grams of ALA. Hemp seed oil is equally rich, offering around 2.5 grams of omega-3s per tablespoon. One standout feature is their omega-6 to omega-3 ratio, which ranges from 2:1 to 3:1, considered ideal for nutritional balance. However, the body’s conversion of ALA to EPA and DHA remains under 15%.
Ease of Incorporation into Meals
Hemp seeds, often called hemp hearts when hulled, have a mild, nutty flavor that complements a variety of dishes. Sprinkle them on oatmeal, blend them into smoothies, or add them to salads for a crunchy texture. They also work well in baked goods like muffins or energy bars and can even replace breadcrumbs in veggie burger recipes. Hemp seed oil is best used as a finishing touch - drizzle it over roasted vegetables or mix it into salad dressings. Avoid heating the oil to preserve its omega-3 content.
Availability and Affordability
Hemp seeds and hemp seed oil are easy to find in grocery stores, health food shops, and online. They’re a budget-friendly option for omega-3s, with prices starting at $11.03 for a 12-ounce bag (365 by Whole Foods Market) and going up to $39.99 for a 5-pound bulk bag (Sincerely Nuts). Buying in bulk or choosing store brands can help reduce costs, making hemp seeds a practical addition to a dairy-free diet.
Additional Nutritional Benefits
A 3-tablespoon serving of hemp seeds offers more than just omega-3s. It provides 9.47 grams of complete protein, containing all nine essential amino acids, along with significant amounts of manganese (99% DV), magnesium (50% DV), and zinc (27% DV). Unlike many other seeds, hemp has very low levels of phytic acid, which may improve mineral absorption. For better protein digestibility, opt for hulled seeds (hemp hearts). If you’re looking to increase your fiber intake, whole seeds are the way to go, offering about 8 grams of fiber per serving compared to just 1.2 grams in the hulled version. To keep hemp seeds fresh, store them in a cool, dark place or refrigerate them after opening.
Hemp seeds’ versatility makes them a fantastic addition to your diet, paving the way for other omega-3-rich options like walnuts, which we’ll explore next.
4. Walnuts
Omega-3 Content per Serving
Walnuts bring a powerhouse of omega-3s to your dairy-free diet, offering variety and impressive nutritional perks. They’re the only tree nut to deliver a meaningful amount of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), making them an excellent choice for meeting your omega-3 needs without dairy. A 1-ounce serving (about 7 walnuts) packs 2.57 grams of ALA, which easily surpasses the daily ALA recommendations for women (1.1 grams) and men (1.6 grams). It’s worth noting that English walnuts are a better option compared to Black walnuts, as the latter only provide 0.76 grams of ALA per ounce.
Ease of Incorporation into Meals
Walnuts are incredibly versatile and can elevate a variety of dishes with their rich flavor and satisfying crunch. Start your day by sprinkling chopped walnuts over overnight oats, porridge, or dairy-free yogurt. For lunch or dinner, toss them into leafy green salads, roasted veggies, or even a kale and mushroom hash for a hearty touch. Crushed walnuts make a great coating for proteins and can even be blended into a flavorful dairy-free pesto with basil, garlic, and olive oil. And don’t forget dessert - they shine in fruit crumbles, dairy-free brownies, or banana bread.
Availability and Affordability
You’ll have no trouble finding walnuts - they’re widely available in grocery stores, health food shops, and online across the U.S. Experts often recommend getting omega-3s from whole foods like walnuts instead of turning to pricey supplements. To keep their delicate omega-3 fats intact, store walnuts in a cool, dry place or refrigerate them after opening.
Additional Nutritional Benefits
Walnuts aren’t just about omega-3s - they’re also a great source of plant-based protein, fiber, magnesium, and antioxidants. Regularly eating walnuts has been associated with improved brain function, sharper memory, lower blood pressure, healthier cholesterol levels, and reduced inflammation.
"These fats are really crucial... they play essential roles in your heart, lungs, and blood vessels" – Amber Young, MS, RDN, Redefined Nutrition
With their impressive nutrition and versatility, walnuts are a fantastic addition to any dairy-free diet. Their nutrient-dense profile naturally leads us to explore other exciting omega-3 sources, like seaweed and algae-based options.
5. Seaweed and Algae-Based Supplements
Omega-3 Content per Serving
If you're on a dairy-free diet, algae-based supplements are a fantastic way to get your omega-3s without any contaminants. These supplements deliver EPA and DHA directly - the same forms of omega-3s you’d find in fish. That means no relying on your body to convert ALA (alpha-linolenic acid), which has a conversion rate of less than 15%.
Most algal oil supplements provide between 400 and 500 mg of combined DHA and EPA per serving, but some high-potency options can go up to 1,210 mg per serving, including 660 mg of EPA and 440 mg of DHA. This makes algae supplements an efficient choice for meeting your omega-3 needs.
"Algae is the original source of omega-3s in the marine food chain. Fish are only rich in omega-3s because they're eating algae." – Amber Young, MS, RDN, Founder, Redefined Nutrition
For those who prefer whole foods, wakame offers around 200 mg of EPA and DHA per 100 g, while dried spirulina contains about 800 mg of ALA per 100 g. To reap the benefits, aim for at least 250 mg of combined DHA and EPA daily.
Ease of Incorporation into Meals
Algae-based omega-3 supplements are super easy to work into your routine. They come in softgel or liquid form, so you can either take them with meals or mix the liquid into smoothies, juices, or other cold drinks. Many brands even add flavors like peppermint or lemon to mask any marine taste and avoid the dreaded "fishy burps" often associated with fish oil. Just remember, algae oils shouldn't be heated to avoid damaging their nutrients.
If you prefer whole seaweed, there are plenty of ways to enjoy it. Use nori sheets for sushi, toss hijiki into soups or stews, or sprinkle dulse powder over your dishes for a savory kick.
Availability and Affordability
You can find algae-based supplements online or in health food stores across the U.S. For example, Sapling Vegan Omega 3 offers 60 softgels for about $24.95 (around $0.42 each) and boasts a 4.7/5 star rating from over 4,000 Amazon reviews. Another option, Nordic Naturals Ultimate Omega Plant-Based, is priced at approximately $48.95 for 60 softgels. Many brands also offer subscription discounts of 10% to 20%.
When shopping, look for products certified under Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and those with a Certificate of Analysis to ensure you're getting a pure and potent product.
Additional Nutritional Benefits
Algae-based omega-3s come with a host of health perks. They support heart and brain health, improve immune and digestive functions, aid joint mobility, and even promote eye health. Plus, since algae are cultivated in controlled environments, they’re free from contaminants like mercury and PCBs that can be found in ocean-sourced products. Many users report noticeable benefits, such as better joint health and lower cholesterol levels, after regular use.
Do We Need Fish Or Fish Oil To Get Enough Omega 3 - Fatty Acids? by Brenda Davis
6. Edamame and Soy Products
Soy products, including edamame, are another excellent plant-based option to diversify your omega-3 intake. While they primarily provide ALA (a plant-based omega-3), the body converts only a small percentage - less than 15% - of ALA into EPA and DHA. Even with this limitation, soy remains a helpful addition to dairy-free diets as a source of omega-3s.
Omega-3 Content per Serving
Here’s a quick look at the omega-3 content in common soy-based foods:
- Edamame (½ cup): 0.28g ALA
- Firm tofu (½ cup): 0.7g ALA
- Boiled soybeans: 1g ALA
- Soybean oil (1 tablespoon): 0.9g ALA
For reference, the recommended daily intake of omega-3s is 1.1 grams for women and 1.6 grams for men.
"Soy foods contain omega 3 and could be a good addition to your vegan diet." – Alyssa Fontaine, RD, Plant-Based Dietitians
Easy Meal Ideas with Soy
Soy products are incredibly versatile, making them easy to work into your meals. Toss shelled edamame into grain bowls, salads, or stir-fries for a quick boost of protein and omega-3s. Firm tofu works well in soups, stir-fries, or as a flavorful addition to marinades. For a simple snack, steaming edamame is a great option. You can also add edamame to stews, chilis, or vegetable soups to enhance both texture and nutrition. If you’re using soy milk or yogurt, choose unsweetened and fortified versions to gain extra nutrients like calcium, vitamin D, and vitamin B12.
Accessibility and Cost
Soy products like edamame, tofu, and soy milk are widely available in most U.S. grocery stores. You can find them in frozen sections, health food aisles, or Asian markets. They’re also budget-friendly, making them an accessible dairy-free alternative. When buying tofu, opt for "calcium-set" varieties to support bone health while enjoying the healthy fats.
More Than Just Omega-3s
Soy products bring a wealth of additional nutrients to the table. They’re a great source of complete plant protein, fiber, magnesium, potassium, folate, and vitamin K. These nutrients make soy a valuable addition to a dairy-free diet. However, soy also contains omega-6 fatty acids, so balance your diet by including other omega-3-rich foods like flaxseeds or chia seeds.
Comparison Table
Below is a breakdown of omega-3 content, serving sizes, and key benefits for various dairy-free options.
| Source | Serving Size | Omega-3 Content | Type | Ease of Use | Additional Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flaxseed Oil | 1 tbsp | 7.26g | ALA | Great for dressings and smoothies; avoid heating | High ALA concentration, but lacks fiber |
| Chia Seeds | 1 oz (28g) | 5.0g | ALA | Sprinkle on oatmeal, yogurt, or use in pudding | Packed with fiber, calcium, and protein |
| Flaxseeds (Ground) | 1 tbsp | 2.35g | ALA | Mix into baked goods or use as an egg substitute | Adds fiber, protein, magnesium, and manganese |
| Hemp Seeds | 3 tbsp (30g) | 2.6g | ALA | Blend into smoothies or sprinkle on salads | Supplies complete protein, iron, and zinc |
| Walnuts | 1 oz (28g) | 2.57g | ALA | Snack on them or add as a salad topping | Contains protein, vitamin E, and magnesium |
| Algal Oil | 1 softgel | 400–500mg | DHA/EPA | Convenient supplement form | Direct DHA/EPA source, toxin-free |
| Tofu (Firm) | 1/2 cup | 0.7g | ALA | A versatile protein for meals | Offers complete protein and, if calcium-set, a good calcium source |
| Edamame | 1/2 cup | 0.28g | ALA | Easy snack or side dish | Provides complete protein, fiber, and folate |
Each source brings something different to the table. Flaxseed oil stands out for its concentrated ALA content - just one tablespoon delivers more than four times the daily ALA requirement for men, though it doesn't contain the fiber or protein found in whole seeds. On the other hand, chia seeds and ground flaxseeds combine omega-3s with valuable fiber and minerals. Walnuts and hemp seeds offer comparable ALA levels while also delivering nutrients like protein, magnesium, and zinc.
For those looking for a direct source of EPA and DHA (without relying on the body's ALA conversion process), algal oil is the go-to option. It's the only plant-based source that provides these essential long-chain fatty acids in a supplement form. Meanwhile, tofu and edamame contribute smaller amounts of omega-3s but shine as versatile, protein-rich options.
A balanced approach works best. Combine sources like ground flaxseeds, walnuts, and algal oil to efficiently meet your omega-3 needs while enjoying a variety of flavors and nutrients.
Conclusion
Getting enough omega-3s on a dairy-free diet is absolutely doable with the right mix of plant-based options. The secret lies in variety - pairing ALA-rich foods like ground flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts with algae-based supplements ensures you're covering all bases. This combination not only provides the essential fatty acids your body needs but also delivers DHA and EPA directly, skipping the inefficient conversion process. It's a simple yet effective way to meet your nutritional needs and support overall well-being.
Omega-3s play a crucial role in maintaining heart health, helping to lower blood pressure and reduce triglycerides. They also support brain function and help combat chronic inflammation, while contributing to healthy cell membranes and bolstering your immune, endocrine, and respiratory systems. With such wide-ranging benefits, making omega-3s a daily part of your diet is a smart move.
For an easy start, sprinkle a tablespoon of ground flaxseeds, chia seeds, or hemp seeds into your meals each day. Use flaxseed oil in cold dishes like salads to keep your ALA intake steady. If you're pregnant, older, or simply want to ensure you're getting enough DHA and EPA, algae-based supplements are a great option - they deliver the same fatty acids found in fish without relying on animal products.
It's also important to pay attention to your omega-6 to omega-3 ratio. Most Americans consume a 20:1 ratio, but aiming for a healthier 4:1 balance can help reduce inflammation. By focusing on these plant-based omega-3 sources and cutting back on processed oils high in omega-6, you'll move closer to that ideal ratio.
FAQs
How can I add flaxseed to a dairy-free diet?
Flaxseed is an excellent source of plant-based omega-3s and fits seamlessly into a dairy-free diet, especially when used in its ground form for better absorption. Try adding 1–2 tablespoons of ground flaxseed to your smoothie, oatmeal, or almond yogurt for a mild, nutty flavor. It’s also a great addition to baked goods like muffins, pancakes, or banana bread. Need a vegan egg substitute? Mix 1 tablespoon of ground flaxseed with 3 tablespoons of water, let it sit for 5 minutes, and you’re good to go.
For savory dishes, sprinkle flaxseed over salads, roasted veggies, or avocado toast. You can even drizzle flaxseed oil into dressings or soups for an omega-3 boost - just make sure not to heat the oil, as that can diminish its nutrients. Since flaxseed is packed with fiber, it’s important to drink plenty of water throughout the day to keep your digestion running smoothly. These easy tweaks let you enjoy the health perks of flaxseed while keeping your meals dairy-free.
What makes algae-based omega-3 supplements a good option compared to other plant-based sources?
Algae-based omega-3 supplements stand out because they deliver DHA (and often EPA) directly - these are the long-chain fatty acids your body requires. On the other hand, plant-based options like flaxseed, chia seeds, and walnuts provide ALA, a short-chain omega-3. The catch? Your body has to convert ALA into DHA and EPA, but this process is notoriously inefficient - less than 10% becomes EPA, and even less turns into DHA.
Algae oil offers a clean, plant-based alternative to fish oil. It provides DHA in a form that's easy for your body to absorb, without the fishy aftertaste or concerns about contaminants. This makes algae supplements a dependable option for people on dairy-free, vegan, or vegetarian diets. While traditional plant-based foods remain excellent sources of ALA and other nutrients, algae-based products fill the gap for those looking to meet their omega-3 needs more effectively.
What are the best omega-3 sources for a dairy-free diet?
Meeting your omega-3 needs on a dairy-free diet is entirely doable by focusing on plant-based sources of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) and, if necessary, algae-based supplements for EPA and DHA. ALA, a type of omega-3 fatty acid, is naturally present in foods like flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts, hemp seeds, soybeans, and canola oil. While your body can convert some ALA into EPA and DHA, this process is limited, so additional sources may be helpful.
To keep your omega-3 intake on track, consider adding ground flaxseed, chia seeds, or walnuts to your daily meals. If you want to increase your EPA and DHA levels without relying on fish, algae-based supplements - such as algal oil - are an excellent vegan and dairy-free alternative. These supplements offer the same heart and brain health benefits as fish oil. By combining ALA-rich foods with optional algae-based supplements, you can confidently meet your omega-3 needs while sticking to a dairy-free lifestyle.



